
While the Big Five theory of personality assumes that personality consists of our essential, unchangeable, innate qualities, the social-cognitive theory of personality argues that personality itself is dynamic (Cervone, Shadel, & Jencius, 2001).

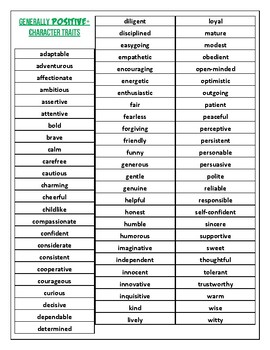
It also states that much of our behavior-what we might consider to be personality-arises as a direct result of social stimuli. This theory reminds us that we are constantly interacting with our social environment. I believe laws should be strictly enforced.Īlthough the Big Five theory of personality is strong and rigorously tested, it's worth thinking about another less-talked-about theory: The social-cognitive theory of personality. I talk to a lot of different people at parties. Openness to experience (versus close-mindedness). This might include creativity, novelty-seeking, thoughtfulness, being rule-free, imaginative, etc.Neuroticism (versus emotional stability). This might include anger, depression, anxiety, hostility, guilt-proneness, emotional intensity, vulnerability, etc.

This might include achievement, autonomy, order, control, rule-consciousness, self-sufficiency, constraint, etc. Conscientiousness (versus undependability).This might include affiliation, cooperation, empathy, friendliness, sensitivity, nurturance, tolerance, warmth, trusting, understanding, etc. This might include activity, assertiveness, attention-seeking, gregariousness, sociability, vigor, etc. And each of these five factors of personality includes hundreds if not thousands of personality traits-traits that are slight variations on an underlying theme (Goldberg, 1993).Īfter much research, a general consensus has been reached (at least among the majority of personality psychologists) that there are five higher-order personality traits (Goldberg, 1993). Each of these five factors is on a continuum where each of us has more or less of the five traits. Unfortunately, the research does not support the Myers-Briggs test or the idea of personality types ( Pittenger, 2005).Īfter decades of research, statistical techniques have largely led researchers back to the five-factor model of personality. For example, you might have heard about the Myers-Briggs Personality measure. And still other researchers suggested that there are personality types. Other early theories proposed more or less than five categories of personality. These five categories appear to be the same regardless of whether personality is measured with self-ratings, observer ratings, or peer ratings (Goldberg, 1993). Early statistical analysis of these common adjectives found that they clumped into five categories. Now we view these adjectives to be examples of personality traits.

For example, we might say someone is responsible, creative, emotional, or outgoing. But even back then, we still used adjectives to describe people. Not too long ago we didn't even know we had personalities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
